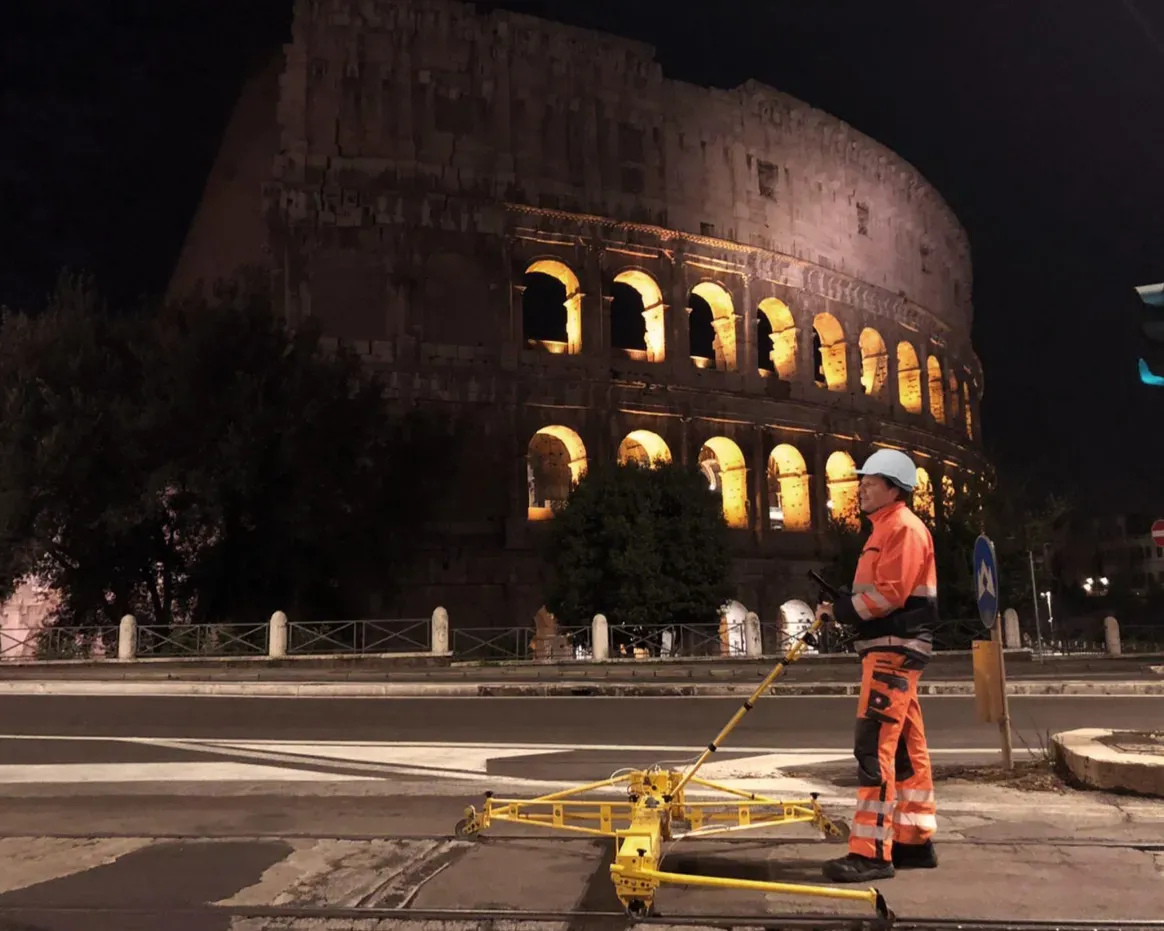
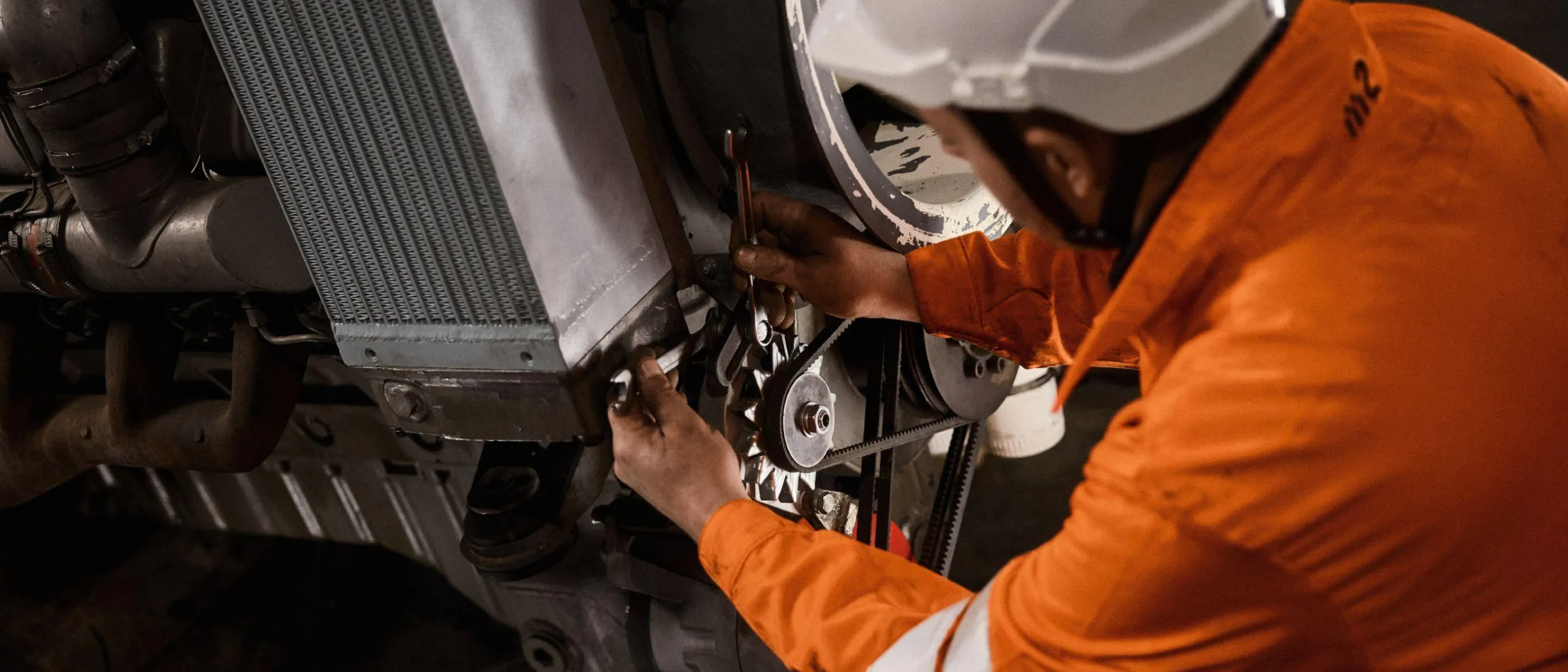
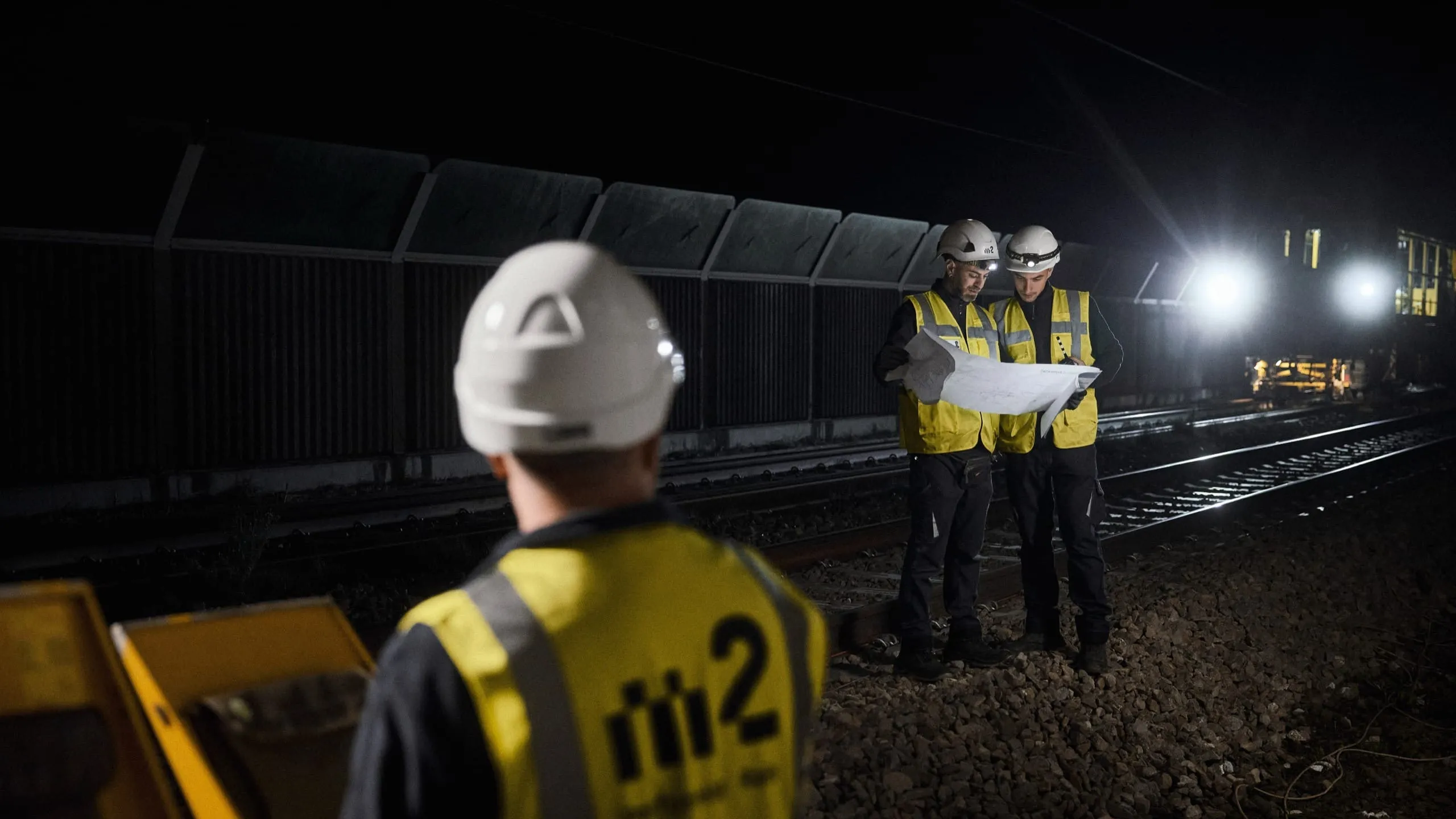
Gleisbaumaschinen warten und bedienen
On-board-Service und Retrofit
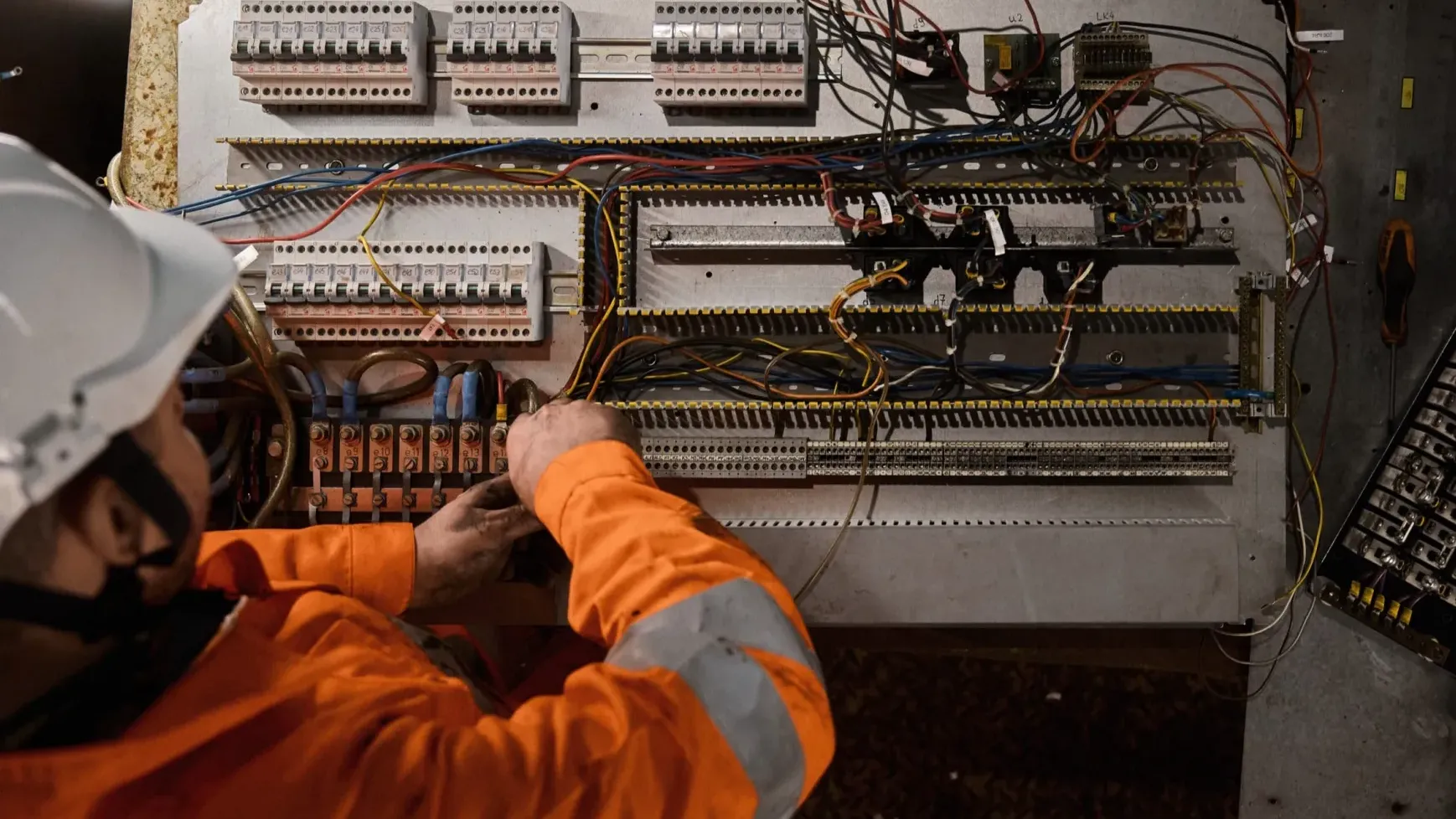
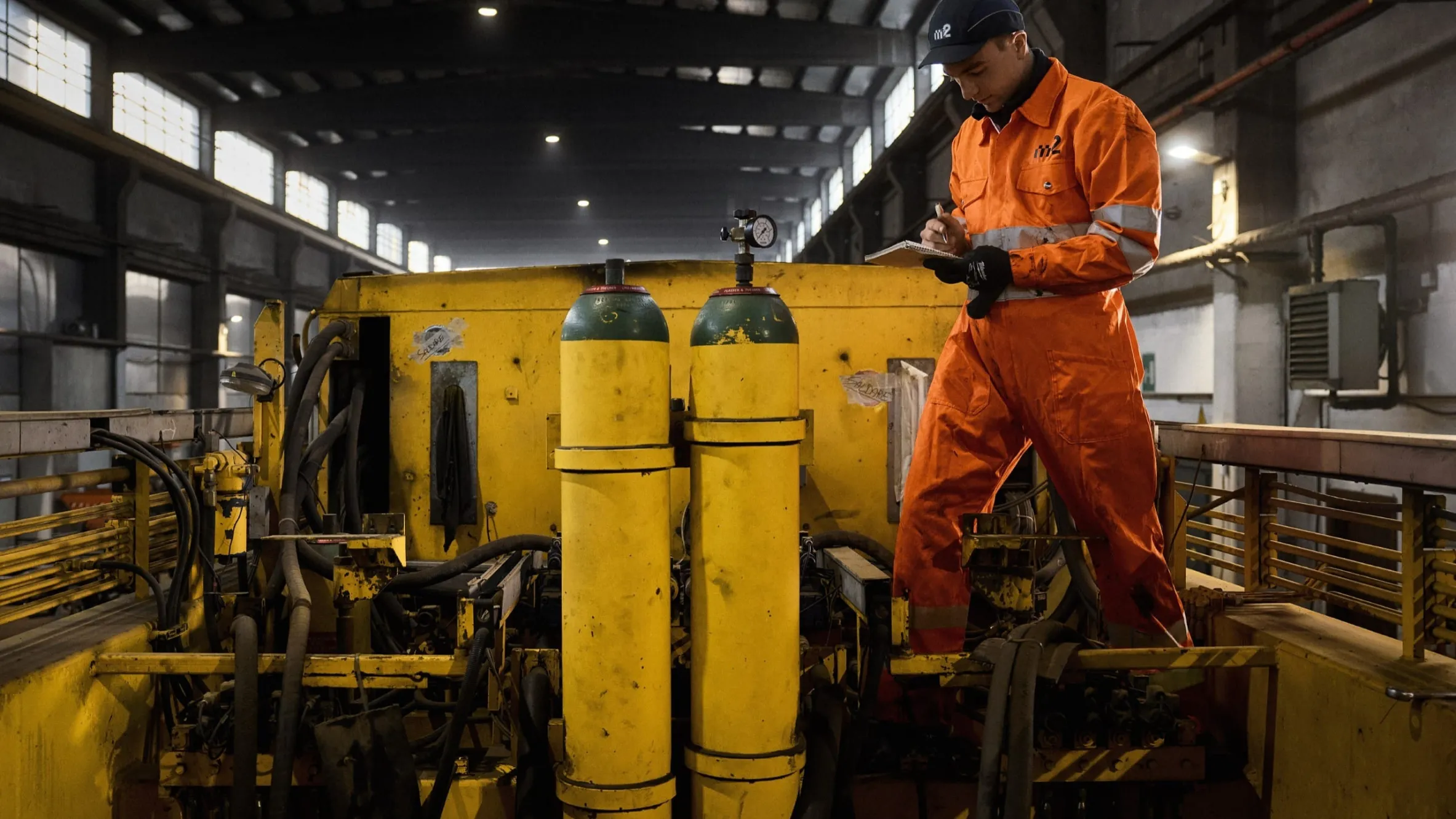
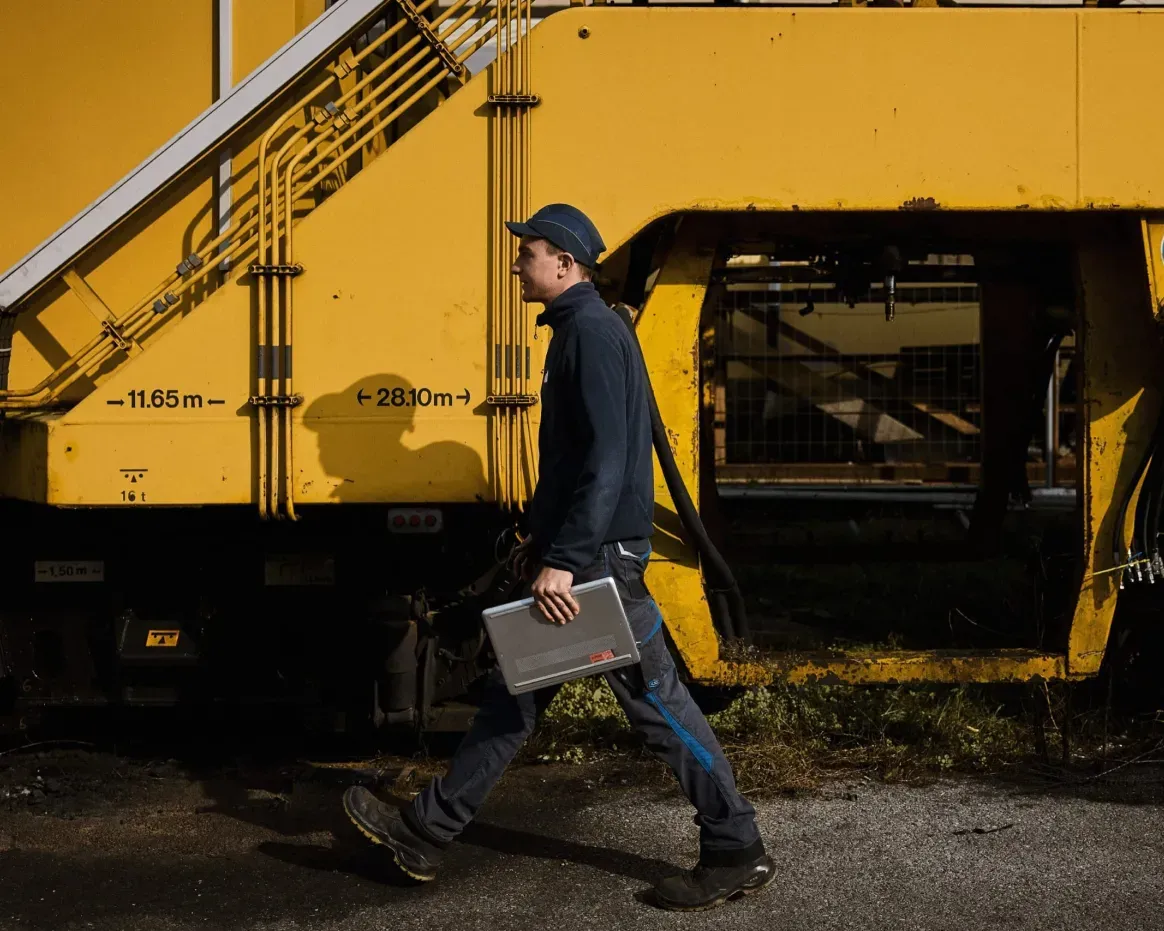
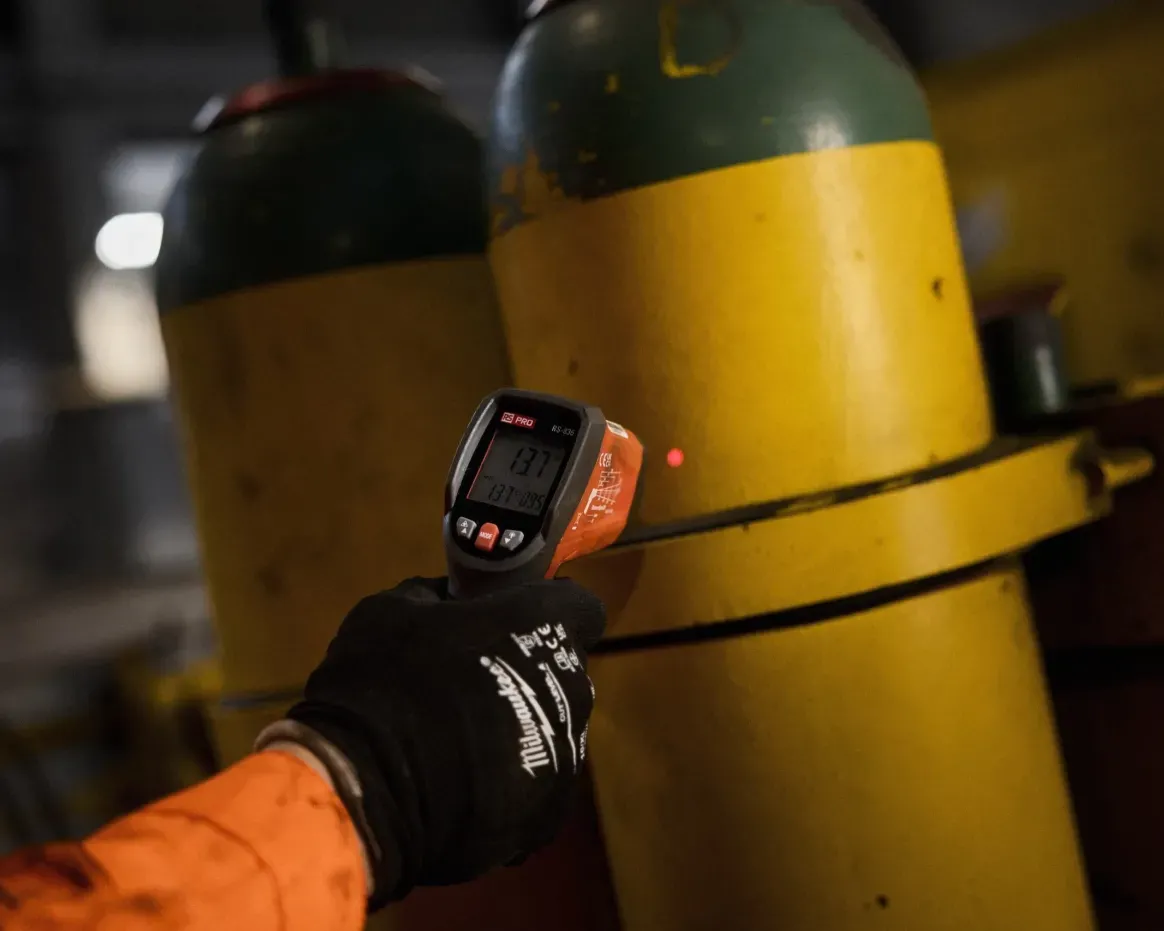
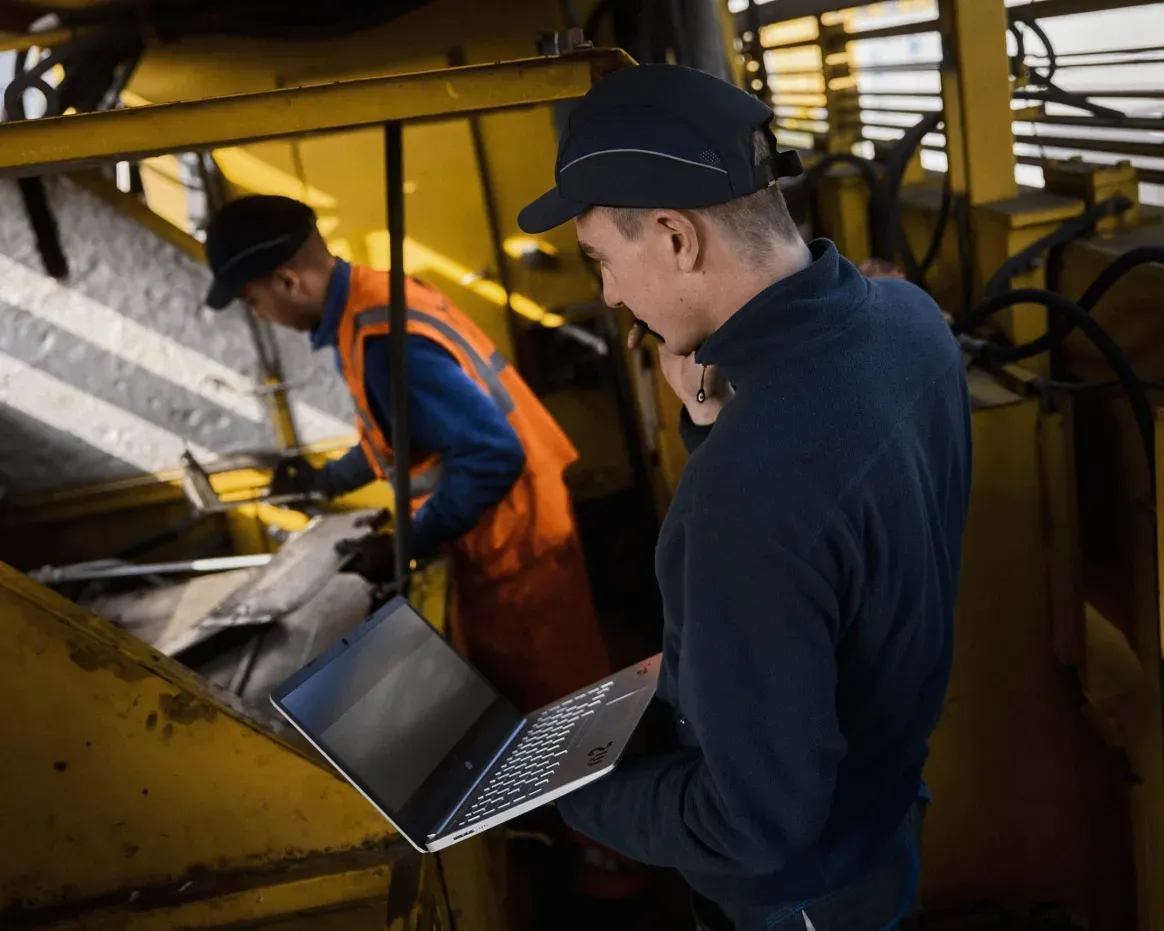
Mit unserem On-Board-Service halten wir Ihre Gleisbaumaschinen einsatzbereit. Vom präzisen Monitoring und Reporting über vorbeugende Wartungsmaßnahmen bis hin zu Reparaturen minimieren wir Ausfallzeiten und maximieren die Leistung. Bei Bedarf übernehmen wir auch die Maschinenführung. Mit unserem Retrofit-Service bieten wir eine kostengünstige Alternative zum Neukauf: Wir zerlegen Ihre Maschine, montieren sie mit hochwertigen Ersatzteilen wieder zusammen und schenken ihr so zusätzliche Betriebszeit. Nachhaltig und kosteneffizient.













